What eats rabbits ?
Rabbit Predators: Introduction
Rabbits are a familiar sight in many parts of the globe, famous for their rapid expansion and felt binding their own space pet domestic / wild animal. Yet their place in the food chain is a precarious one, as they are food for several predators. The rabbit food chain is an important aspect of ecosystems, and the animals that eat them, include predators that help balance populations.
The top carnivores in the mammalian world that hunt the hare
Wolves Eating Rabbits
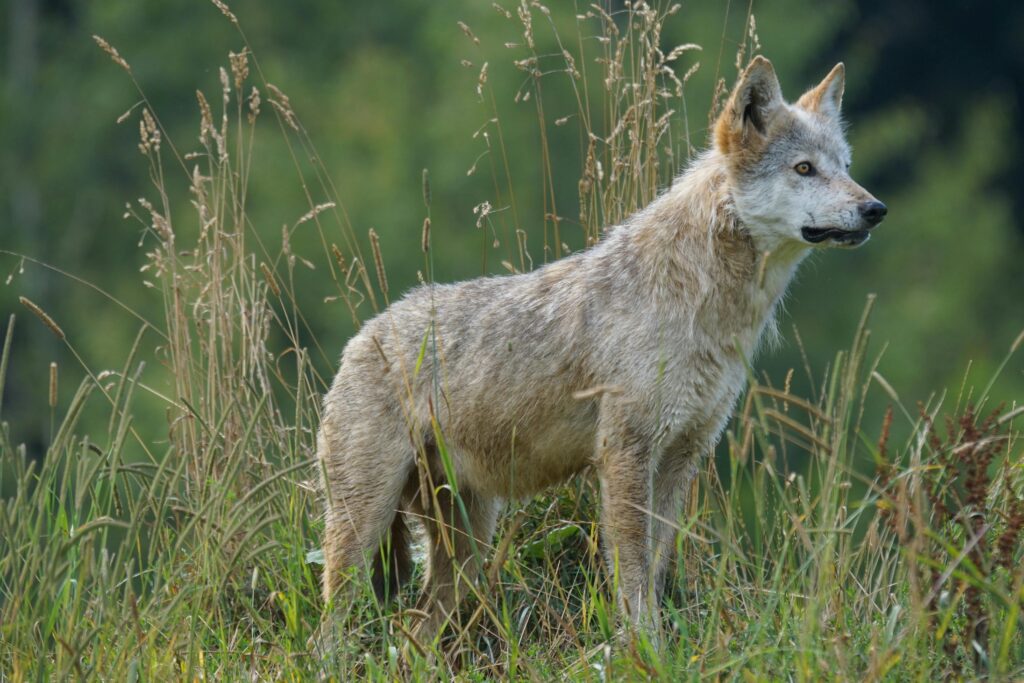

Wolves, top predators of the wildlife, they hunt in packs. Their primary targets are mule deer and elk, but they will also hunt rabbits, particularly when larger prey is in short supply. While rabbits are fast and agile and can be hard for wolves to catch, wolves.work together and can outlast their quarry: it’s hard for the rabbit, in the end, to outrun the pack.
Foxes and Rabbits
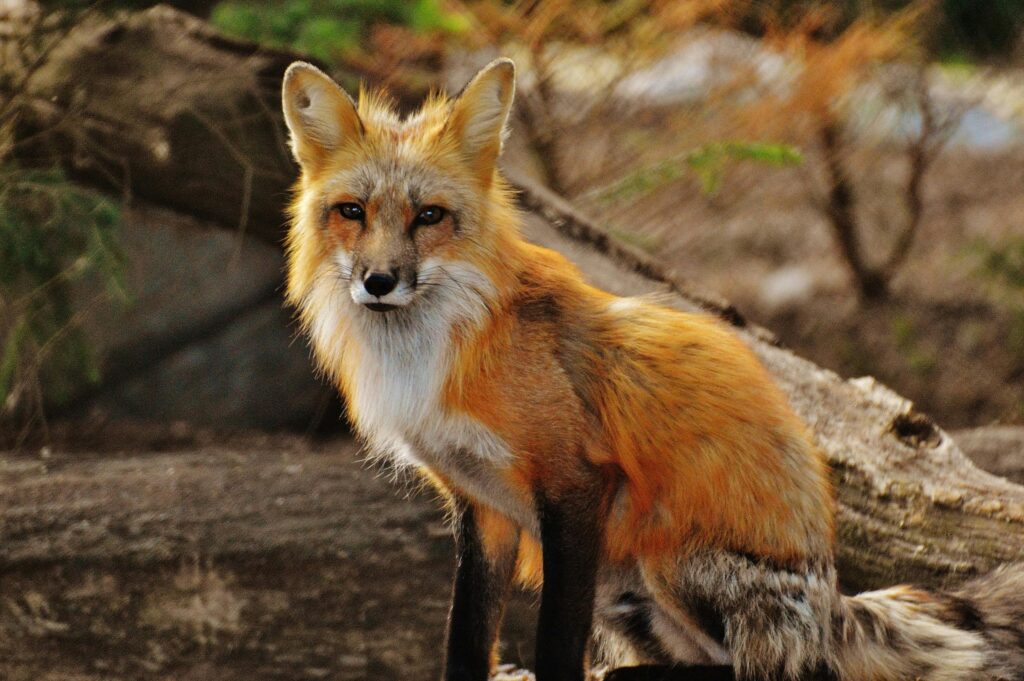

Foxes are opportunistic feeders, eating small mammals, birds, and insects. Rabbits constitute a large portion of their diets because they are plentiful and easier for foxes to catch than larger prey. With the help of their stealths and speed, foxes ambush the rabbits and with a single pounce, they attack them.
Wild Dogs Hunting Rabbits
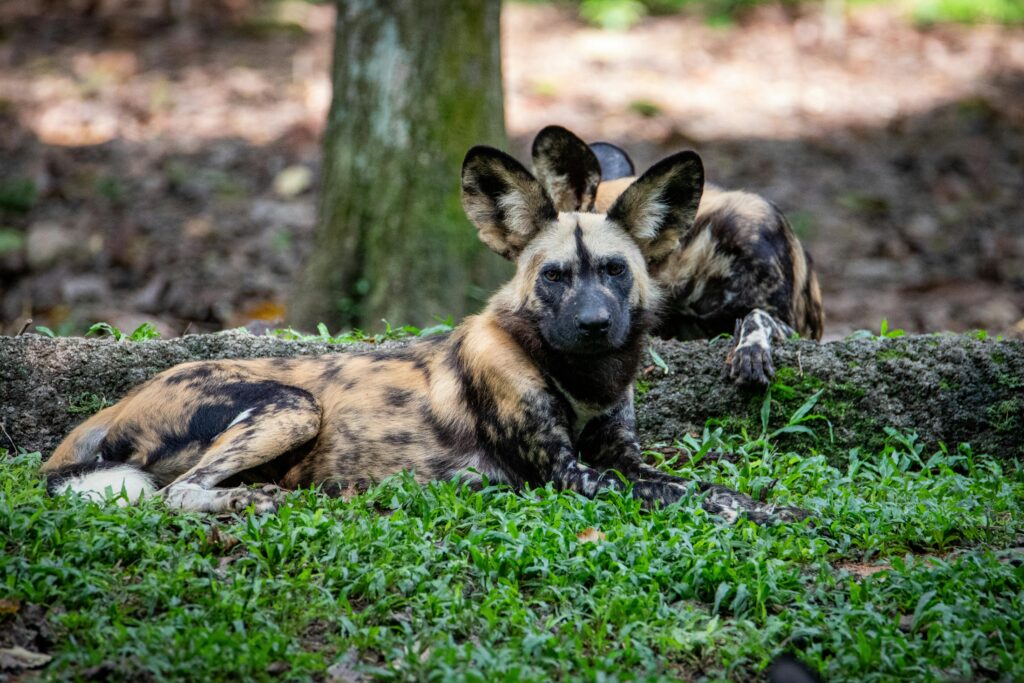

Such as coyotes and dingoes in a variety of environments. They eat a variety of foods, from small mammals to larger animals. Wild dogs often hunt rabbits and will use their sharp sense of smell and hearing to find and pursue them. Usually, the chase is a mix of speed and strategy, in which wild dogs collaborate to surround and kill their catch.
Bobcats and Rabbits
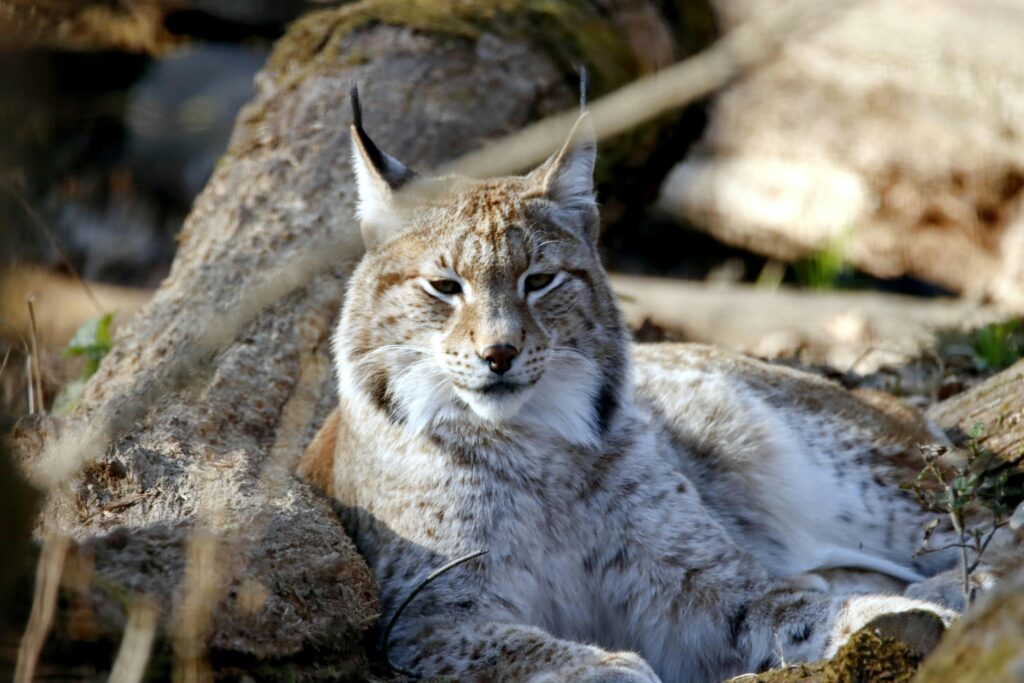

Bobcats are solitary hunters that thrive in habitats with underbrush, which gives them cover while stalking prey. Two prey items that make up a huge portion of a bobcat’s diet are rabbits, a widespread prey source, and the many types of deer, which are riskier and larger.
SUMMARY OF THE SOLUTION Snaring is efficient as favorite prey are captured with no meat wasted, cats can travel through sparsely populated terrain, and only one cat would need to be snared, e.g. capture a bobcat by snaring it on top of the prey it attacks,
and Bobcat’s natural attack behaviors would result in either direct fatality of the attack or additional eatable prey resulting from the intensity of the attackBobcats hunt rabbits; Their claws and legs serve as potent weapons and they use them to ambush their prey.
Rabbits Preyed on by Birds of Prey
Eagles Eating Rabbits
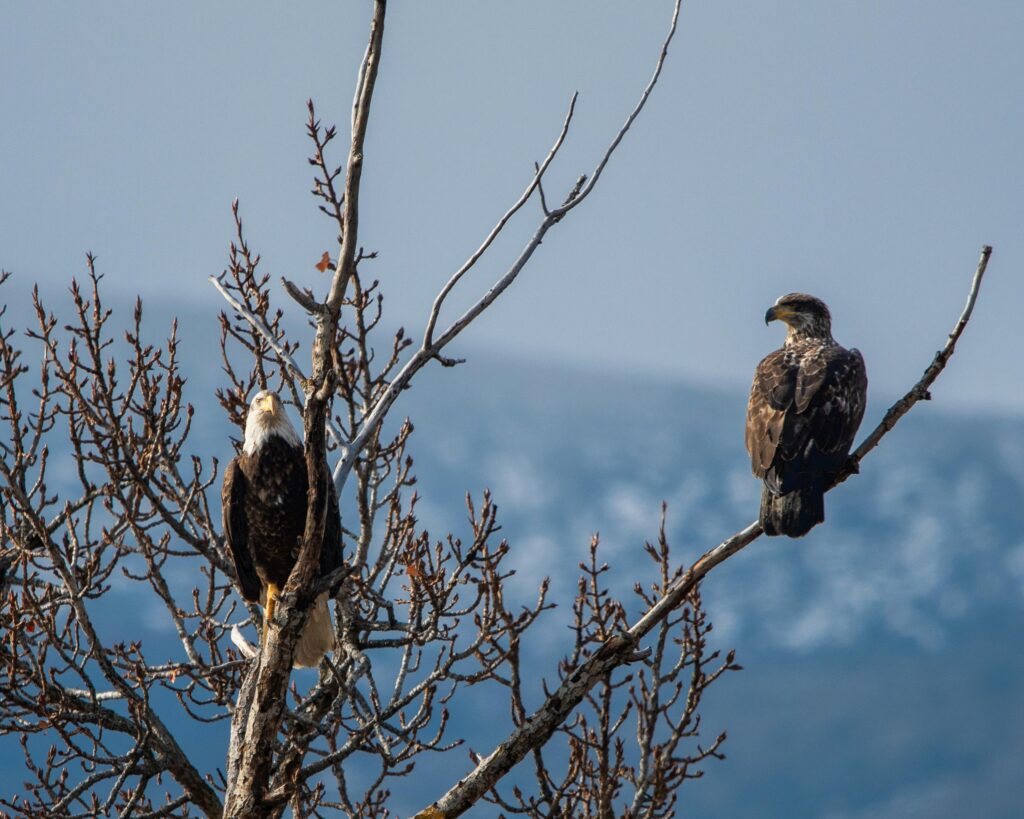

Eagles are strong predatory birds with superb eyesight, so they can see rabbits from lofty heights. They are characterized by their majestic flight and the ability to dive bomb at great speeds to seize their quarry. Eagles most commonly hunting rabbits in open spaces, swooping down to grab them with their talons.
Hawks and Rabbit Predation
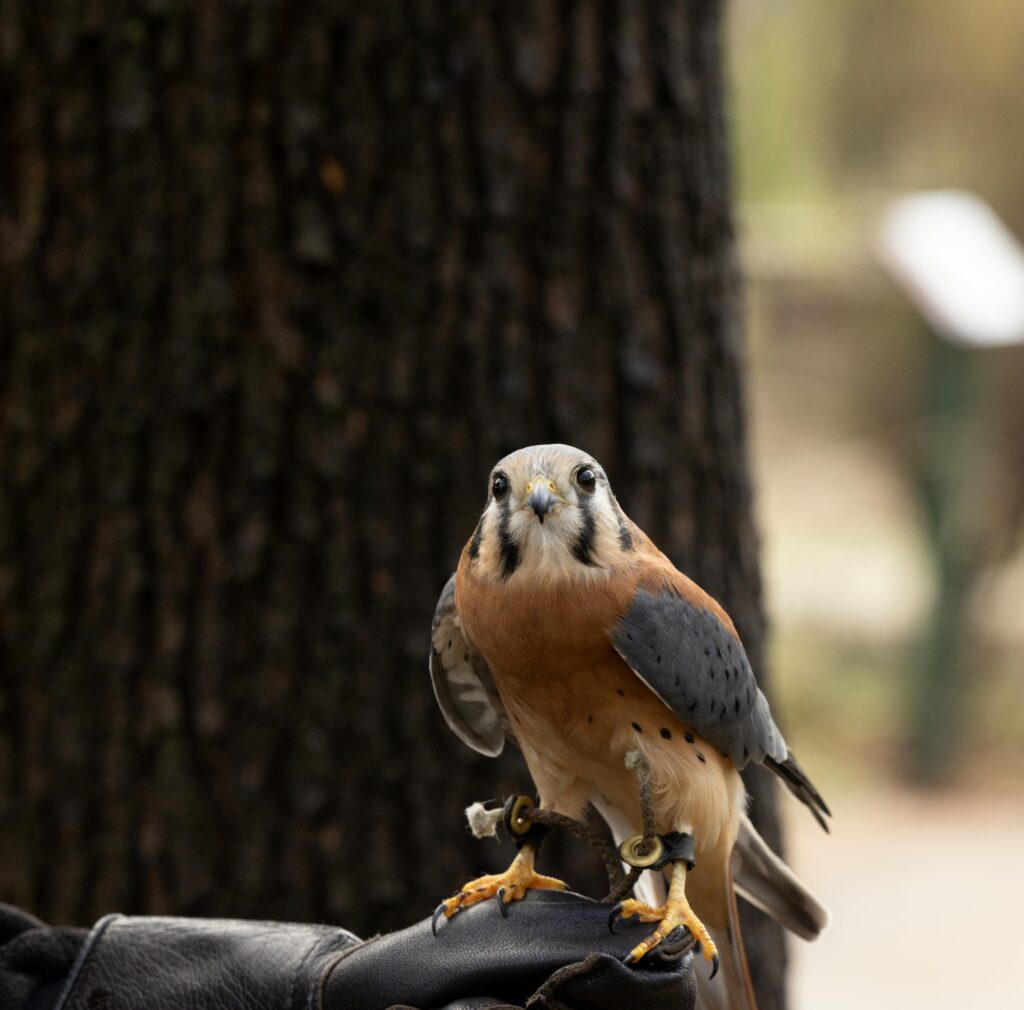

Another group of raptors also eats rabbits: the hawks. They can also hunt forest, grass, or even urban areas. After swooping down onto the ground, hawks tend to rely on their keen talons to snag rabbits, often taking them by surprise from their perch or while flying low to the ground.
Owls Hunting Techniques
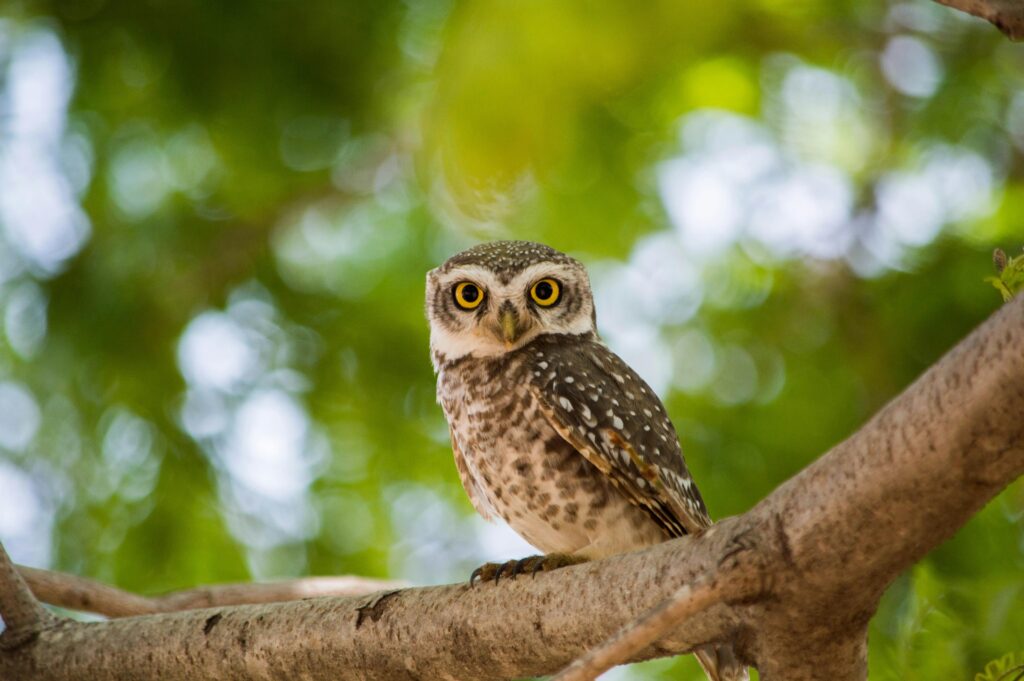

Owls, as nocturnal hunters, have an edge over their diurnal predators. Their quiet flight and keen hearing make rabbits a prime target. Owls do this catch rabbits at dusk, seizing rabbits off the ground with their sharp talons. In low-light situations, they are adept hunters because of their silent flight and superior night vision.
The Top Reptilian Threats to RabbitsBold-Snake Prey: An Overview of Various Snakes and Other Reptiles that Set Their Eyes on Rabbits
Snakes Eating Small Mammals
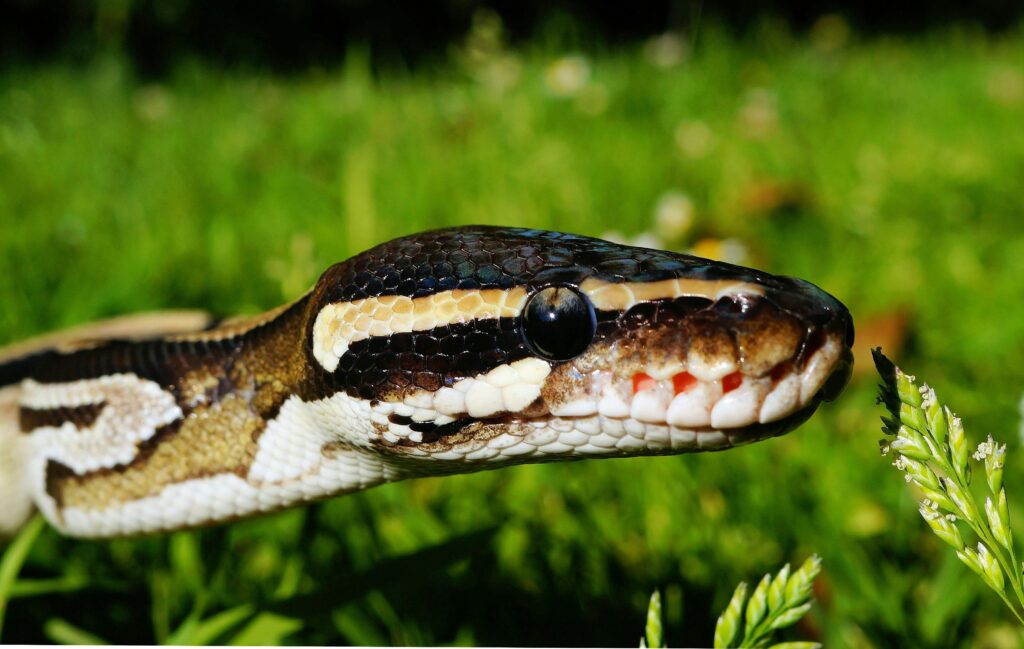

Many species of snake are important predators in an ecosystem — a select few even target small mammals like rabbits. Some large snakes, such as pythons and boas, can eat rabbits whole. These reptiles rely on their strong squeezing abilities to capture and kill rabbits and eventually swallow them whole.
Snakes Feasting on the Young of their Prey
Smaller reptiles such as some varieties of lizards and young snakes might feast on baby, or kit, rabbits. These reptiles prey on juvenile hares, which are more susceptible to capture and provide meal-sized sustenance. There are a number of reptiles that are common in the habitats of the rabbits.
Constrictors and Their Prey
Constrictors (boas and pythons) dead prey by wrapping their powerful-bodied around it and squeezing until it suffocates. Being small enough to be overpowered by these serpents, rabbits are occasional prey for constrictors. This form of predation is especially well-suited for mammals such as rabbits, who depend on their speed and agility to evade predators.
Humans as Predator in the Case of Rabbits
Rabbits as Human Food Source
Have hunted rabbits for food for thousands of years. Rabbits are a sustainable source of protein, especially in rural areas where a red meat or wild game might not be available. Their flesh is low-fat and nourishing and therefore a good source of food. Hunting rabbits for meat is a practice still observed in many cultures, aiding in controlling rabbit populations.
Hunting Practices and Effects on Rabbit population
Rabbit populations are greatly affected by hunting practices. Hunting, regulated in certain areas, helps keep the population of rabbits from overgrowing and destroying their habitats.
But without regulations, hunting can contribute to declines in rabbit populations and can therefore disrupt the balance of ecosystems. Hunting rabbits sustainably is important to keep their population healthy and their position in the food chain intact.
Sustainably Harvesting Small Game
Hunting in a sustainable manner for wild rabbit is would not over harvest the rabbit populations or destroy their habitat. That means following hunting seasons, controlling how many rabbits are (permitted to be) taken and employing techniques that reduce suffering. Sustainable hunting is important so that rabbits will continue to be part of the ecosystem and that humans may have food and recreational opportunity.
How Predation Influences Rabbit Populations and Their Ecosystem
Harmonic Interaction Between Prey and Predators
A relationship as old as time, and certainly the basis for much of ecosystem dynamics in predators and prey. Predators contribute to controlling rabbit populations, preventing overgrazing and depletion of vegetation.
The natural world will keep on spinning when its inhabitants are in balance, which is critical for biodiversity and ecosystems health. With no natural predators, mainland rabbit population can spiral out of control, resulting in overgrazing and habitat damage.
Population Control of the Rabbit through Natural Medias
One of the main methods of keeping rabbit populations balanced is natural predation. Predators like wolves, foxes, raptors, and reptiles are important to keeping rabbit populations in line. This acts as a natural population control, allowing ecosystems to function properly without depletion of resources or hindering the competition of other species.
The Ecological Role of Predator[edit]
Instead, predation is a natural process and one of the most important processes in an ecosystem. It Limits numbers of prey species and therefore acts as a check to prevent one prey species from dominating an ecosystem and crowding out other species.
Predators not only impact ecosystems by causing prey species deaths but also affect prey species behavior and distribution, influencing ecosystem structure. Predation if studied properly helps us to understand the intricacies of nature.
Conclusion:
Understanding the Balance of Nature’s Food Chain with Rabbits
Even if they reproduce fast, rabbits are at the heart of the ecosystems, most are even food for other animals. Their predators — from mammals and birds of prey to reptiles and humans — play a key role in maintaining nature’s balance. This knowledge can help inform conservation efforts and hunting regulations to protect both the rabbit population and its predators.
Understanding the role rabbits play in nature means coming to terms with what rabbits themselves represent in the food chain, which is, in fact, a life outside our species — a tension that only makes sense when we move away from Anthropocentrism or Humanicentricism.
Yuns Legdm is a passionate advocate for pet care and the founder of this website, dedicated to providing valuable information for fellow pet lovers and veterinary professionals worldwide. With a deep love for animals, Yuns created this platform to connect passionate pet owners with expert insights from veterinarians around the globe.
This website grows with you—the passionate pet owners and veterinary experts—creating a trusted space where knowledge, experience, and love for animals come together. Whether you’re seeking advice on pet health, nutrition, or general well-being, this platform is here to support you on your journey of responsible and loving pet care.